 Home
Home
 Back
Back
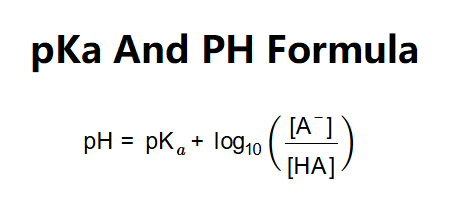
Definition: This calculator determines the pKa of a buffer solution based on the pH and the concentrations of a weak acid [HA] and its conjugate base [A⁻], using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Purpose: It helps chemists, students, and researchers calculate pKa from pH for buffer solutions, useful in chemistry, biology, and environmental science for understanding acid-base equilibria.
The calculator uses the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the pH value, input the acid and salt concentrations with their units, and click "Calculate." Results show pKa, pH, pOH, [H⁺], and [OH⁻], with values < 0.00001 displayed in scientific notation.
Details: Understanding pKa and pH is crucial for analyzing buffer systems, chemical reactions, and biological processes. Accurate calculations ensure reliable pH control in experiments and applications.
Tips: Enter a valid pH value (0 to 14), input positive concentrations with consistent units (M, mM, or µM), and click "Calculate." Ensure concentrations are accurate for precise pKa calculation.