 Home
Home
 Back
Back
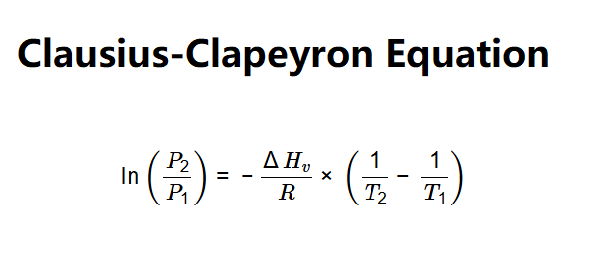
Definition: This calculator determines the molar enthalpy of vaporization (\(\Delta H_v\)) of a substance based on initial and final temperatures and pressures, using the Clausius-Clapeyron equation.
Purpose: It is used in chemistry and thermodynamics to predict vapor pressure changes during phase transitions, aiding in process design, material analysis, and understanding phase equilibria.
The calculator uses the Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the initial temperature (e.g., 25°C), final temperature (e.g., 100°C), initial pressure (e.g., 101325 Pa), and final pressure (e.g., 760 Torr). The calculator converts units, uses the Clausius-Clapeyron equation to compute \(\Delta H_v\), and outputs it in J/mol, kJ/mol, cal/mol, and kcal/mol.
Notes on Units: Ensure pressures are positive and non-zero, and temperatures are physically meaningful (e.g., above absolute zero). The molar enthalpy of vaporization is typically positive, reflecting the energy required for vaporization.
Details: Vapor pressure and enthalpy of vaporization are critical for understanding phase changes, predicting boiling points, and designing processes involving evaporation or condensation, such as distillation, refrigeration, and material processing.
Tips: Input initial and final temperatures and pressures with their respective units. Ensure all values are positive and appropriate for the substance. The calculator assumes ideal behavior and uses the gas constant \(R = 8.314 \, \text{J/(mol·K)}\). Results are approximate for non-ideal substances or complex phase transitions.