 Home
Home
 Back
Back
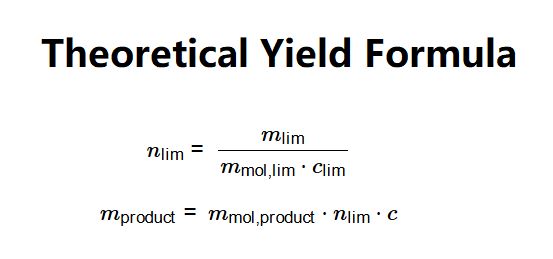
Definition: This calculator determines the theoretical yield of a chemical reaction based on the mass of a reactant, its molecular weight, and stoichiometry, step by step.
Purpose: It is used in chemistry to calculate the maximum amount of product that could be formed in a reaction, assuming 100% efficiency, aiding in reaction planning and analysis.
The calculator follows these steps, using the theoretical yield formula:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the mass of the limiting reagent (e.g., 10 g), molecular weight of the limiting reagent (e.g., 18 g/mol for water), stoichiometry of the limiting reagent (e.g., 1), stoichiometry of the desired product (e.g., 1), and molecular weight of the product (e.g., 36 g/mol). The calculator performs the steps above and outputs the moles of the limiting reagent and theoretical yield in various units.
Details: Theoretical yield represents the maximum product possible, providing a benchmark for reaction efficiency, helping identify losses, and guiding experimental design in chemical synthesis.
Tips: Input the mass, molecular weights, and stoichiometry values with their units. Ensure all values are positive, and molecular weights and stoichiometries are non-zero to avoid division errors. Stoichiometry values should reflect the balanced chemical equation for accurate results, with the limiting reagent and desired product specified correctly.