 Home
Home
 Back
Back
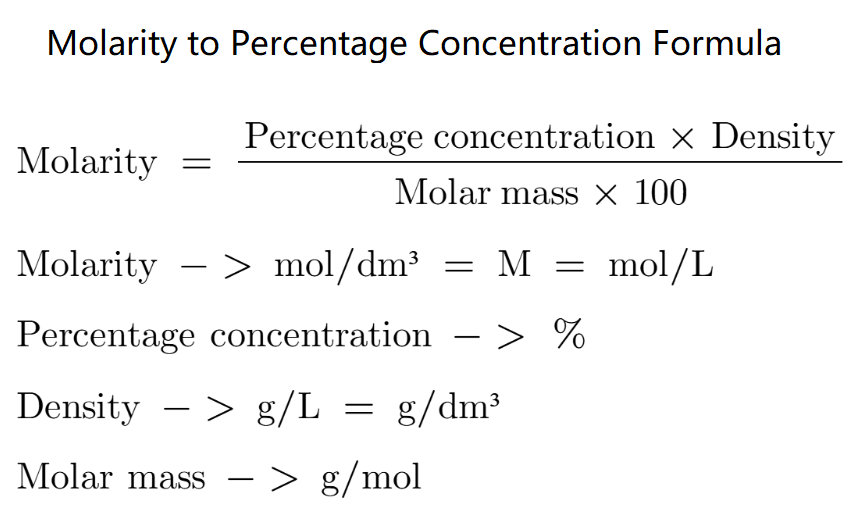
Let's say we have a 10% solution of Ammonia (NH₃) with a density of 0.91 g/mL.
Using the formula:
M = (10 × 0.91 × 1000) / (17.03 × 100)
After calculating, the molarity (M) is:
M = 5.34 mol/L
| Substance | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|
| Ammonia | 17.03 |
| Acetic acid | 60.05 |
| Ethanol | 46.07 |
| Formaldehyde | 30.03 |
| Glucose | 180.16 |
| Hydrochloric acid | 36.46 |
| Hydrogen peroxide | 34.01 |
| Nitric acid | 63.01<|control704|> |
| Phosphoric acid | 97.99 |
| Potassium hydroxide | 56.11 |
| Sodium chloride | 58.44 |
| Sodium hydroxide | 40.00 |
| Sulfuric acid | 98.08 |
The molar mass of a substance is usually equal to its molecular weight. Remember to use the unit g/mol.
To determine the molecular weight of water (H₂O):
If you know the molarity, molar mass, and density of a solution, you can calculate the percentage concentration using the following formula:
The result will be in percent (%).