 Home
Home
 Back
Back
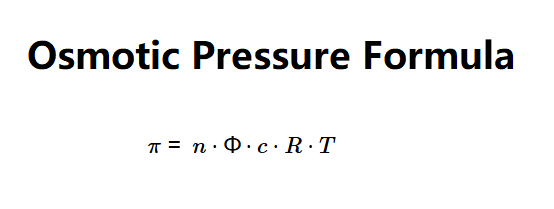
Definition: This calculator determines the osmotic pressure (\(\pi\)) of a solution based on the number of ions (\(n\)), osmotic coefficient (\(\Phi\)), concentration (\(c\)), and temperature (\(T\)), using the osmotic pressure formula.
Purpose: It is used in chemistry and biology to predict osmotic pressure in solutions, aiding in osmosis studies, cell physiology, and industrial processes like desalination and drug delivery.
The calculator uses the osmotic pressure equation:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the number of ions (e.g., 2 for NaCl), osmotic coefficient (e.g., 1 for ideal solutions), concentration (e.g., 0.1 mol/L), and temperature (e.g., 25°C). The calculator converts units, computes \(\pi\) in Pa, and outputs it in all specified pressure units.
Notes on Units: Ensure \(n\), \(\Phi\), and \(c\) are positive and non-zero, and temperature is above absolute zero. Concentration must be in mol/L, mol/mm³, mol/cm³, mol/m³, mol/cu in, or mol/cu yd, converted to mol/L for calculation.
Details: Osmotic pressure drives osmosis, critical for cell function, water purification, and biological processes, influencing hydration, plant physiology, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Tips: Input \(n\), \(\Phi\), \(c\), and \(T\) with their respective units. Ensure all values are positive and physically meaningful. Results are approximate for ideal solutions; adjust for non-ideal behavior or solute interactions if needed.