 Home
Home
 Back
Back
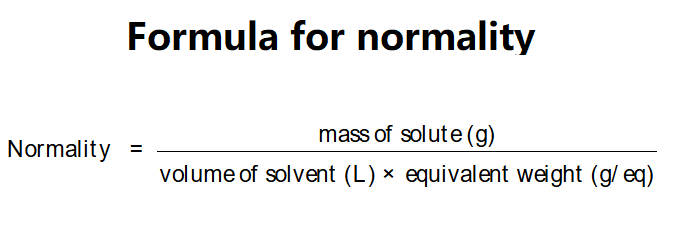
Definition: This calculator determines the Normality (N) of a solution, which measures the concentration of a substance (acid or base) in equivalents per liter, based on the weight of solute, volume of solvent, and equivalent weight.
Purpose: It is used in acid-base chemistry to quantify solution strength for neutralization reactions, titrations, and chemical preparations.
The calculator uses the following formula:
Explanation: Enter the weight of solute (e.g., 10 g), volume of solvent (e.g., 1 L), and equivalent weight (e.g., 36.5 g/eq for HCl). The calculator converts units to grams and liters, then computes Normality.
Details: Normality is crucial for understanding reactive concentrations in solutions, especially in titrations and neutralization processes where the number of equivalents matters.
Tips: Input the weight of solute, volume of solvent, and equivalent weight with their respective units. Ensure all values are positive and equivalent weight reflects the substance’s valence for accurate results.