 Home
Home
 Back
Back
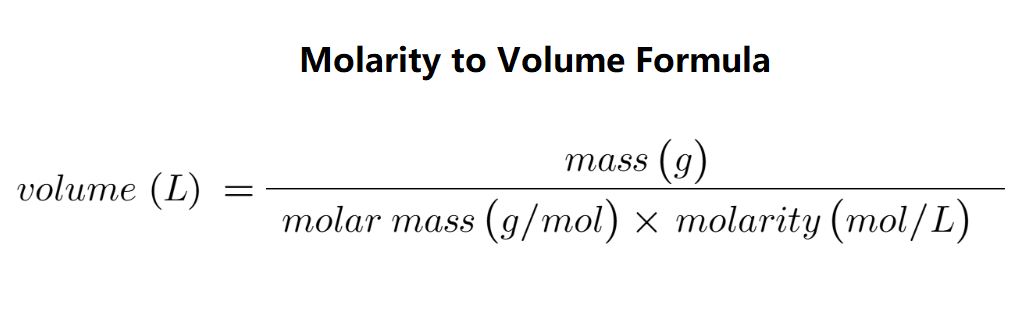
Volume (L) is the amount of solution required to dissolve a given mass of solute. It is calculated using the formula:
V = \( \frac{mass}{molar\_mass \times molarity} \)
Example: You have 5 g of NaCl with a molar mass of 58.44 g/mol and a solution molarity of 0.1 mol/L.
Using the formula:
V = \( \frac{5}{58.44 \times 0.1} \) = 0.855 L
Thus, you need 0.855 L of solution to dissolve 5 g of NaCl.