 Home
Home
 Back
Back
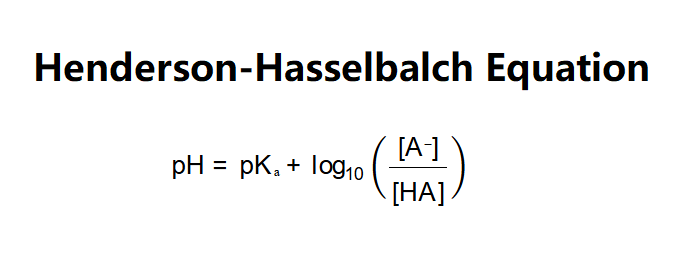
Definition: This calculator uses the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to determine the pH of a buffer solution based on the concentrations of the conjugate base [A⁻], the acid [HA], and the acid dissociation constant (Kₐ).
Purpose: It is widely used in chemistry and biology to predict the pH of buffer systems, aiding in the preparation of solutions with specific pH values.
The calculator applies the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
Explanation: Enter the conjugate base concentration (e.g., 0.1 M), acid concentration (e.g., 0.1 M), and Kₐ (e.g., 1.8 × 10⁻⁵ for acetic acid). The calculator computes pKₐ from Kₐ and calculates the pH.
Details: This equation is essential for understanding buffer capacity and maintaining stable pH levels in chemical reactions, biological systems, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Tips: Input the concentrations of [A⁻] and [HA] with their units (e.g., M, mM), and the Kₐ value. Ensure Kₐ is positive and concentrations are valid to avoid calculation errors.