 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator determines the pH, [H⁺] concentration, and [OH⁻] concentration of a solution based on its pOH value, with customizable units for [H⁺] and [OH⁻].
Purpose: It helps chemists, students, and researchers analyze the acidity or basicity of aqueous solutions, useful in chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
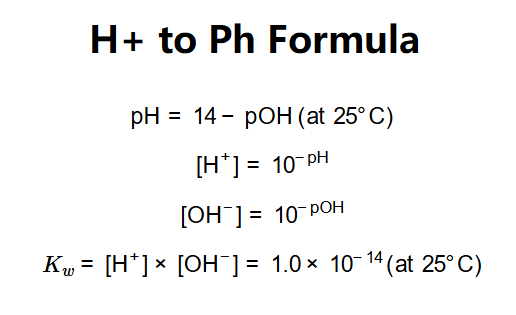
The calculator uses these relationships:
Where:
Explanation: Enter a pOH value, select units for [H⁺] and [OH⁻] (M, mM, µM, or nM), and the calculator computes pH, [H⁺], and [OH⁻] in scientific notation, assuming standard conditions (25°C).
Details: Understanding pOH, pH, and ion concentrations is crucial for assessing solution acidity or basicity, biological processes, industrial applications, and environmental conditions. These values guide chemical reactions, buffer design, and health-related analyses, with units like mM or µM often used in biochemical contexts.
Tips: Enter a positive pOH value, select units for [H⁺] and [OH⁻] (M, mM, µM, or nM), and click "Calculate." Results show pH (to 2 decimal places), [H⁺], and [OH⁻] (in scientific notation, e.g., 1.00000e-12, with selected units).