 Home
Home
 Back
Back
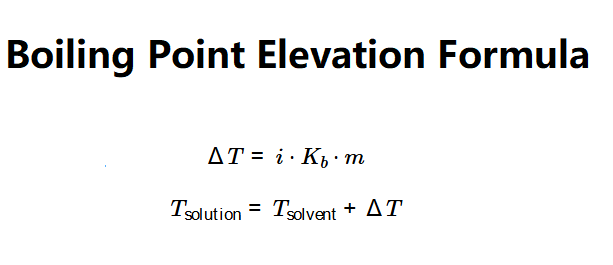
Definition: This calculator determines the boiling point elevation (\(\Delta T\)) and the boiling point of a solution (\(T_{\text{solution}}\)) based on the boiling point of a pure solvent, the ebullioscopic constant, and the molality of the solution.
Purpose: It is used in chemistry to predict how the boiling point of a solvent changes when a solute is added, aiding in solution preparation, colligative property studies, and industrial processes.
The calculator uses the boiling point elevation formula:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the boiling point of the pure solvent (e.g., 100°C for water), ebullioscopic constant (e.g., 0.512 °C·kg/mol for water), and molality (e.g., 3 kg solute/kg solvent). The calculator converts units, computes \(\Delta T\), and calculates \(T_{\text{solution}}\) in °C, °F, and K, displaying them in separate sections.
Details: Boiling point elevation is a colligative property, critical for understanding solution behavior, designing distillation processes, and ensuring safety in chemical and industrial applications where boiling points are modified by solutes.
Tips: Input the boiling point of the pure solvent, ebullioscopic constant, and molality with their respective units. Ensure all values are positive, and the ebullioscopic constant is appropriate for the solvent. The calculator assumes a van’t Hoff factor of 1 (non-dissociating solute); adjust if the solute dissociates (e.g., electrolytes).