 Home
Home
 Back
Back
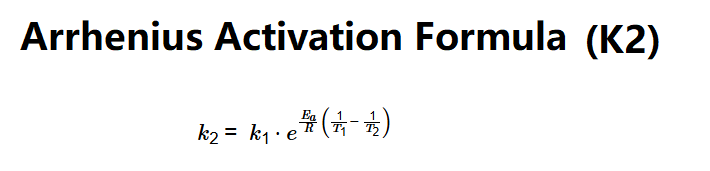
Definition: This calculator determines the reaction rate constant (\(k_2\)) at Temperature 2 (\(T_2\)) using the Arrhenius equation, based on the reaction rate constant at Temperature 1 (\(k_1\) at \(T_1\)), activation energy (\(E_a\)), and \(T_2\).
Purpose: It is used in chemistry to predict reaction rates at different temperatures, aiding in reaction kinetics analysis and experimental design.
The calculator uses the Arrhenius equation:
Explanation: Enter Temperature 1 (e.g., 298 K), Temperature 2 (e.g., 308 K), Reaction Rate Constant 1 (e.g., 0.1 L/sec), and Activation Energy (e.g., 50 kJ/mol). The calculator converts units, uses the gas constant (R = 8.314 J/(K·mol)), and computes \(k_2\) in various units (L/sec, L/min, L/hour, L/day).
Details: The rate constant (\(k\)) quantifies reaction speed, influenced by temperature and activation energy, critical for understanding and optimizing chemical reactions under varying conditions.
Tips: Input Temperature 1, Temperature 2, Reaction Rate Constant 1, and Activation Energy with their respective units. Ensure all values are positive and units are consistent for accurate results. T2 should typically be higher than T1 for standard applications, and Activation Energy should reflect the reaction’s energy barrier.