 Home
Home
 Back
Back
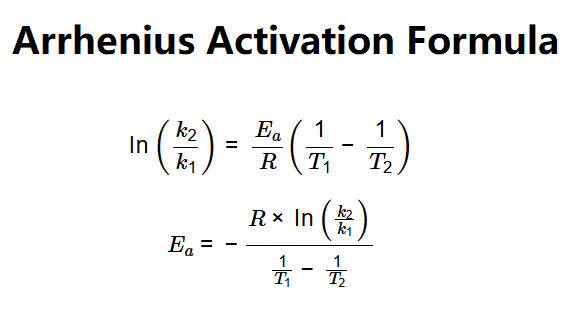
Definition: This calculator determines the activation energy (Ea) of a chemical reaction using the Arrhenius equation, based on two different temperatures and their corresponding reaction rate constants.
Purpose: It is used in chemistry to analyze the energy barrier a reaction must overcome, helping predict reaction rates at different temperatures.
The calculator applies the Arrhenius equation for two temperatures:
Explanation: Enter the two temperatures (e.g., 298 K and 308 K) and their corresponding reaction rate constants (e.g., 0.1 L/sec and 0.2 L/sec). The calculator converts units, uses the gas constant (R = 8.314 J/(K·mol)), and computes activation energy in various units (J/mol, kJ/mol, MJ/mol, cal/mol, kcal/mol).
Details: Activation energy indicates the minimum energy required for a reaction to proceed, influencing reaction rates, temperature dependence, and catalyst effectiveness in chemical processes.
Tips: Input the two temperatures (e.g., 25°C and 35°C) and their reaction rate constants with their respective units. Ensure temperatures are positive, reaction rates are positive, and units are consistent for accurate results. T2 should typically be higher than T1 for standard applications.